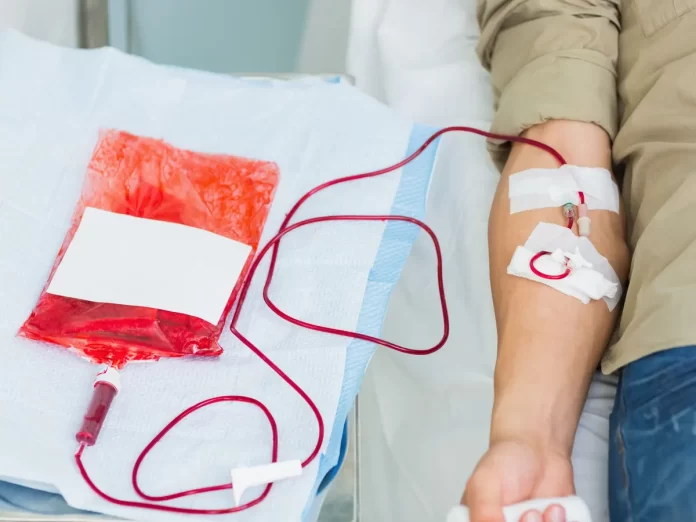
A person is typically able to resume most of their daily routines within a couple of hours after the blood donation. There are a variety of methods to help the body recuperate.
Certain drinks and foods such as coffee and tea can aid in recovering from the donation of blood. Additionally, there are certain things to avoid immediately following a blood donation.
This article will will look at the length of time it takes to recover and what you should do following the donation, how to do to minimize the risk of negative effects and when you should see an expert.
Table of Contents
Time to recover
A typical donation donor donates all blood. It is composed of red cells, the white cell, platelets and plasma.
After donating all blood the recipient usually is able to relax for around 15 minutes at Trusted Source. A person’s attendant can provide water, juice or food items to prevent or ease any discomfort or dizziness.
When a person is at a point of readiness and is ready, they can resume the majority of their normal routines, usually within a couple of hours.
The body produces about the equivalent of 2 million cells per second. However, it could take several weeks to replenish one pint taken in a blood donation. However, very only a few suffer any symptoms from the absence of blood.
The patient must have a minimum of 8 weeks between donation so that they can ensure their body is given the time to heal.
What should you eat following a the blood donation?
The blood donation process lowers the levels of essential nutrients that are present in within the body. Through drinking and eating certain food items, one can aid in the recovery of their body.
Did You Know: 5 Vegetables That Are Good For Healing
Iron
The blood is a rich source of iron and every donation could result in the loss of up to 200 – 250 milligrams of iron.
Consuming iron-rich food can aid in replenishing levels of iron in the blood. Foods high in iron include:
- Red meat
- Spinach and Leafy Greens
- Broccoli
- fortified cereals
Vitamin C aids the body absorb iron, and it’s also recommended to consume foods that are high in vitamin C including bell peppers, citrus fruits and tomatoes.
Anyone who gives blood often may be benefited from iron supplements.
B vitamins
As iron B vitamin such as B-2, B-6, as well as B-9, aid in the creation of new red blood cells. The most common sources of B Vitamins are::
- leafy greens
- dairy products
- Liver
- potatoes
- bananas
- Breakfast cereals fortified with vitamins
- Orange juice
People who are vegan or vegetarian diets might benefit by taking a B vitamin supplement, especially if they find it difficult to absorb enough nutrients from their diet.
Liquids
The process of donating blood eliminates bodily fluids. It is possible to restore these fluids through drinking broth, water and herbal tea.
It is recommended that the American Red Cross suggests drinking an additional 4 glasses or 32 ounces of liquid within the very first 24-hours following making a blood donation.
What should you avoid following a the donation of blood?
The process of donating blood generally does not alter a person’s routine. However, it could restrict what an individual is able to do immediately following the procedure.
The reduction in red blood cells implies that less oxygen is circulating throughout the body. This means that the person must stay clear of intense activities immediately following a donation. This includes:
- manual labor
- Heavy lifting
- cardio exercises
The remainder of the day after having donated blood, it’s generally recommended to stay away from all activities that can cause heart rate elevated.
In the future, a person is able to gradually return to exercise or heavy lifting. The gradual return to these activities will help to minimize any negative consequences of blood loss.
A person must refrain from drinking alcohol within the first 24-hours following a donation.
Adverse effects
Lightheadedness or dizziness
A few people experience dizziness or fainting after donating blood. This is due to the decreased quantity of blood that is circulating in the body results in a temporary decrease in the blood pressure.
Certain preventive measures can be helpful, like drinking plenty of water prior to giving.
Any person who is experiencing lightheadedness or dizziness should stop what they’re doing and lie or sit down. Relax and take deep, slow breaths until the problem goes away. The feet can be raised to assist.
Begin activities slowly, and avoid activities that may be risky because of someone feeling disoriented or off balance.
Bleeding
Once a blood donation has been complete, a nurse will put a bandage on the site in which the needle was placed. They can use gentle pressure in order to assist in letting the blood clot as well as to heal the area.
If blood in a patient isn’t clotting quickly it may be necessary to take a rest. To prevent bleeding be sure to keep the bandage in place and not use the arm whenever it is.
In the event that there’s bleeding at the area Apply pressure and elevate the arm above the head for approximately five minutes till the bleeding ceases.
When the wound is closed then remove the bandage, and clean the area using detergent and warm water. Repeat this process regularly until the wound is completely healed.
Soreness and bruises
A few individuals suffer from bruising around the site of insertion. It happens because the skin’s tissue continues to flow slightly following the insertion.
If the bruising creates pain, cold compressions could aid. One can also take prescription painkillers for pain, like Acetaminophen (Tylenol). Anyone who is planning to donate platelets must avoid using aspirin during the two days prior to the donation.
Tiredness
A little fatigue is common after the donation of blood, but certain people are more susceptible to this than others.
If you feel exhausted after donating blood should take a break until they feel more comfortable.
Drinking plenty of fluids and replenishing mineral and vitamin levels can help to reduce fatigue.
When should you see a doctor?
Most of the time, the negative consequences of donating blood are minor, if anyone observes any.
Anyone who has the same symptoms for a long time is advised to see a doctor. This includes:
- persistent lightheadedness or fatigue
- bleeding that is hard to manage
- either tingling, pain, or numbness of the arm
- The symptoms are sudden and often a sign of a bacterial infection like swelling or fever
Certain health conditions can make blood of a person unfit to donate to other people. The person should notify the center of donation in case they experience some of the following:
- a sudden fever or cough within four weeks of donating
- jaundice, hepatitis or tuberculosis or malaria within three months of the time of
Summary
Donating blood is an easy and efficient way to assist other people.
After a few hours following the donation, an individual will usually be able to resume their usual routine.
There are many ways that can help the body recover. For instance:
- drinking plenty of fluids to hydrate
- eating foods that are iron-rich as well as vitamins B and C
- Do not engage in strenuous activities, like cardio exercises at least for one day
Acute adverse reactions to giving blood is not common. But, anyone who is suffering from persistent or extreme health issues after donating blood must consult an expert physician or the center for donation guidance.